Original BACnet MS/TP data link specification only supports NPDU length up to 501 bytes, which is much shorter than 1497 bytes of Ethernet and IP data link. It limits transmission performance, increases complexity on application layer, especial when two IP/Ethernet networks are conjoined by a MS/TP network.
Extended frame was designed to solve this problem. The detail could be found here. Briefly, this addendum added two new frame types as:
- 32: BACnet Extended Data Expecting Reply
- 33: BACnet Extended Data Not Expecting Reply
Frame type 32 is extended from frame type 5 (BACnet Data Expecting Reply), the special of it is that it is encoded by COBS and the NPDU length it carried is in range of 502 to 1497 bytes.
In the same way, frame type 33 is extended from frame type 6 (BACnet Data Not Expecting Reply)
Extended frame support was added into BACnet standard since revision 16. There are still lot of devices installed or on the market that do not support it. The interoperability between extended frame capable devices and legacy device is discussed below.
- Non-router legacy device and extended frame capable device: Because all messages sent to legacy device are application layer message, the “Max APDU Length Accepted” from Device object property or confirmed service request primitive should be respected, the NPDU length will not exceed 501 bytes. So there are no problem with this configuration.
- Legacy router and extended frame capable device: NPDU that should be relayed to other network through legacy router with length over 501 bytes will be discarded, no reject-message-to network with reason “Message Too Long” will be responded. Even more, the “Max APDU Length Accepted” of legacy router may be determined by other port that has a NPDU length larger than 501 bytes (It is allowed by standard), so NPDU for local application layer sent to legacy router will still possibly be carried by extended frame and discarded. So this configuration may cause problem in field.
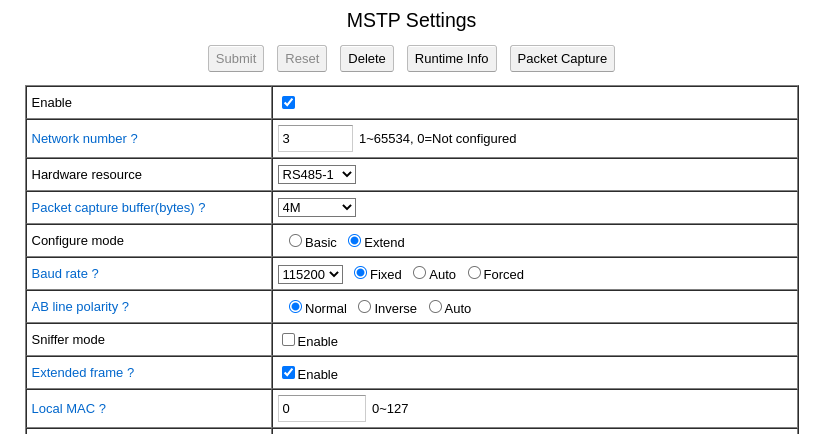
BACRouter supports extended frame from very early version. From firmware version 3.18, we introduced “Extended frame” option on BACRouter’s MS/TP configuration, if there are legacy router that does not support extended frame on the bus, this option should be disabled to avoid Interoperability issues.
It’s worth noting that even “Extended frame” option is disabled, unlike legacy router, BACRouter will still be interoperable with extended frame capable devices.
(Screenshot has been updated on Aug 5, 2021. Because extended frame is mandatory from standard revision 16, from firmware 4.13, we move this option to extended configure mode.)