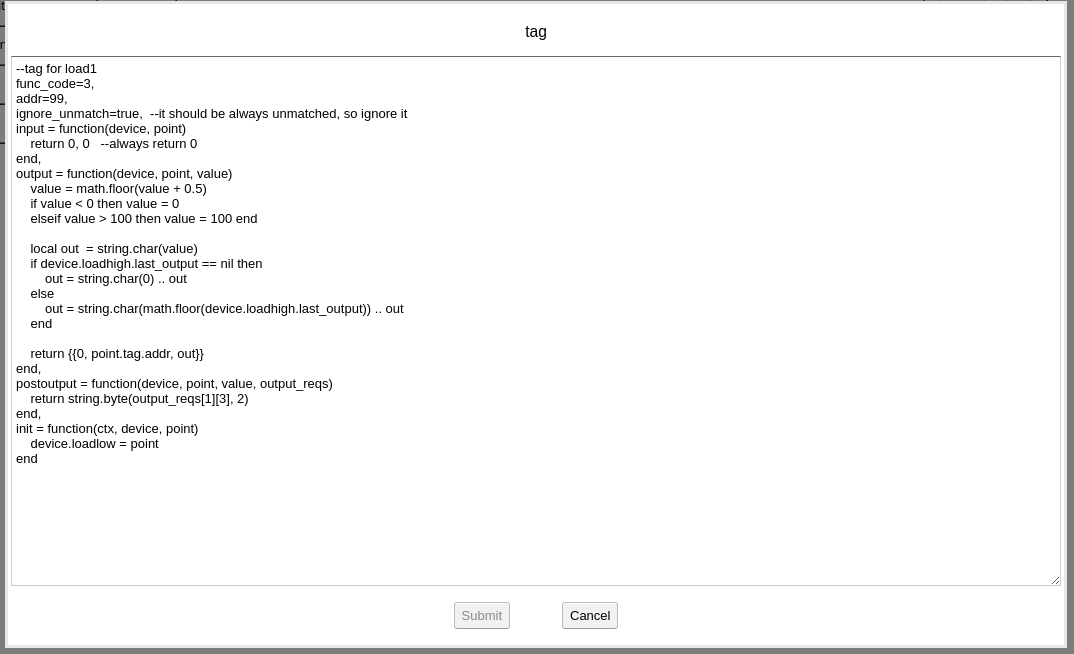
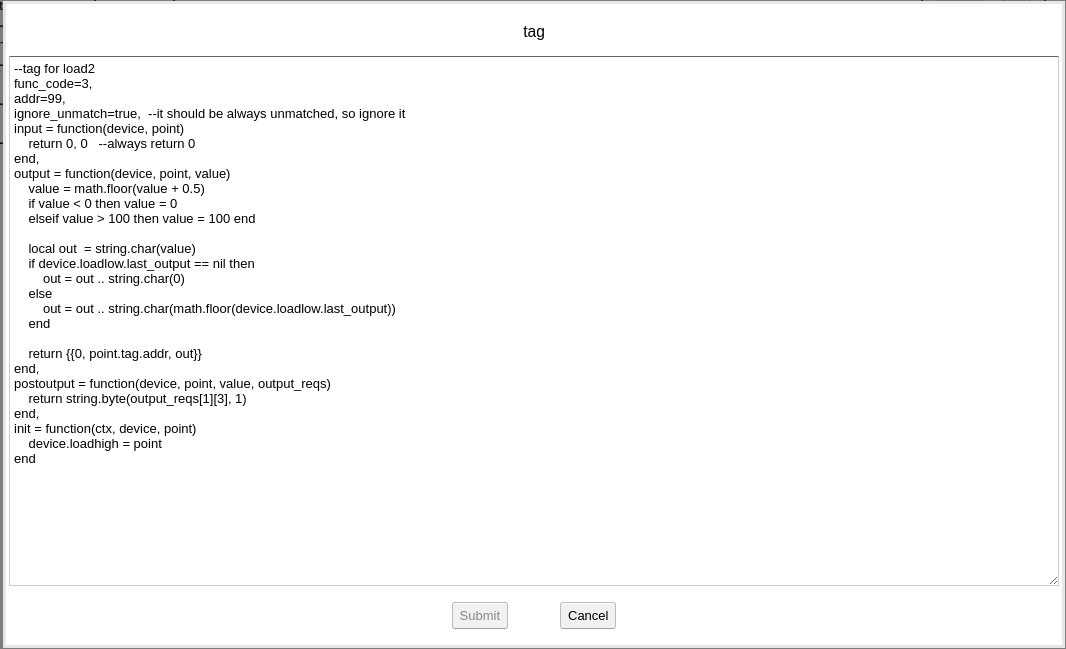
Background
Most serial protocols in BAS domain are based on UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter), e.g. Modbus, MS/TP.
The data stream consists of bytes. Each byte is a UART frame with 4 elements: start bit, 5 to 9 data bits, parity bit if has, 1 or 2 stop bits. Wikipedia for reference.
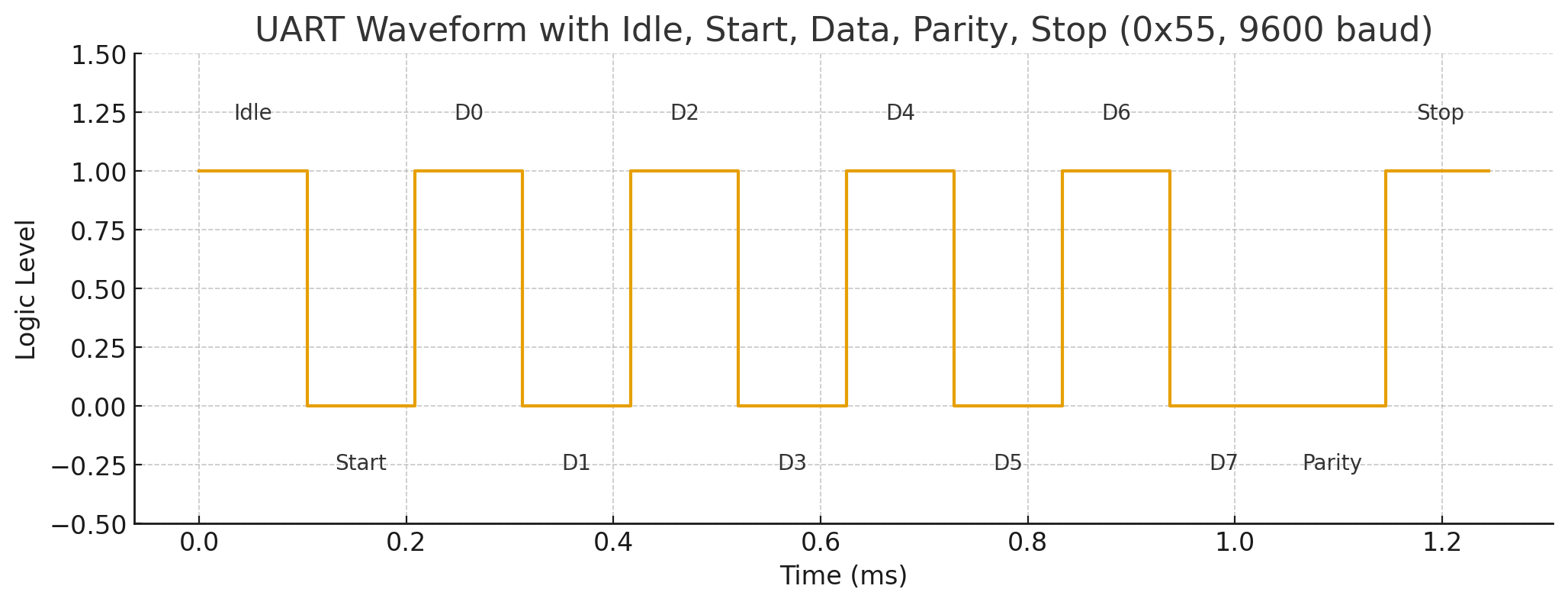 The basic algorithm inside UART decoder includes bit sampling and start bit detection, they all affect performance of noise immunity.
The basic algorithm inside UART decoder includes bit sampling and start bit detection, they all affect performance of noise immunity.
Bit Sampling
There are three most common sampling algorithms: single sampling, majority vote, debounce.
Single Sampling
It is the most easy method that samples at the middle of bit. It is very sensitive to noise.
Majority Vote
A optimized sampling method is to take several samples near the middle of bit, then determine the value by majority vote.
In practice, a common design is using 16 times over sampling, 3 samples will be taken on 8th, 9th, 10th sample clock. The value is determined by at least 2 samples with identical value. But if the width of noise signal is wider than 1/16 bit, 2 false values may be sampled.
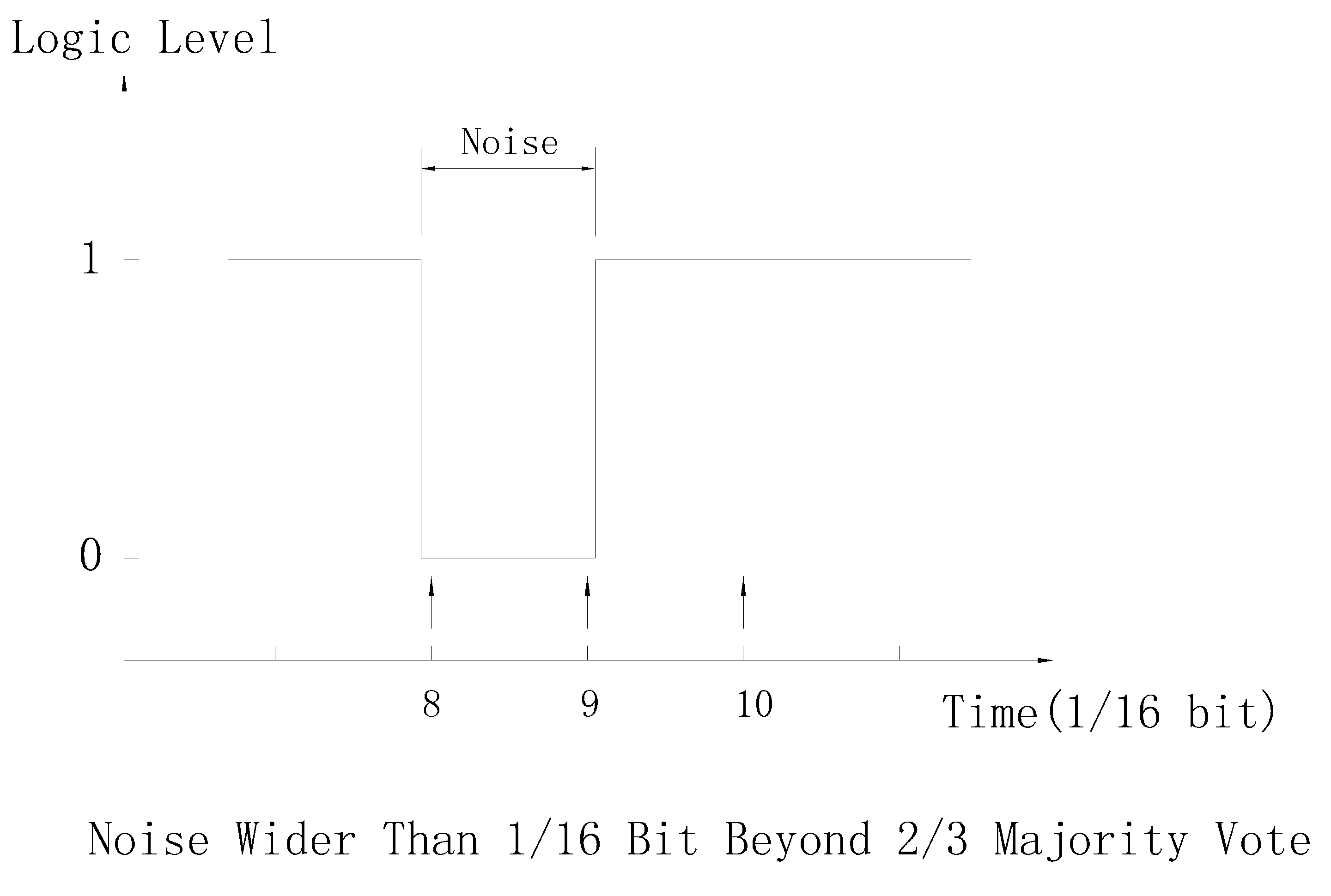 Debounce
Debounce
It’s another over sampling method. If the debounce time is 2 samples, only 2 consecutive samples have same value, the value will be confirmed, otherwise old value will be kept, so single sample noise will be filtered. But if the width of noise signal is wider than 1 sample, 2 consecutive false values may be sampled.
Start Bit Detection
Detection of start bit is critical for decoder to synchronize with sender. That is where “Asynchronous” coming from. There are 3 common detection algorithms on market: falling edge, falling edge with start bit validation, complicated others.
Detect Start Bit By Falling Edge
This method recognizes falling edge as start bit, no more validation will be taken. It is unguarded to noise. For a RS485 bus in idle state, electromagnetic interference is easy to cause noise signal leading to false start bit.
Detect Start Bit By Falling Edge With Start Bit Validation
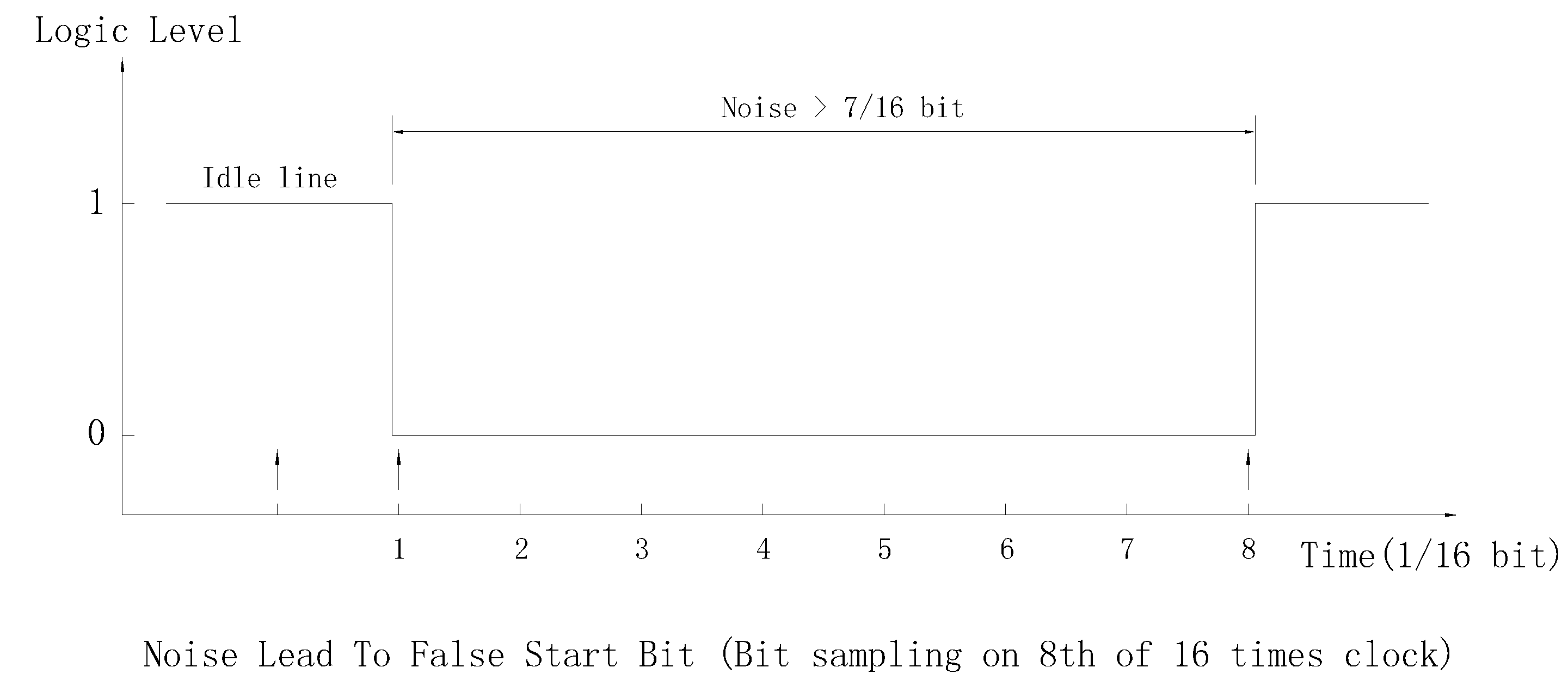
This method is mainstream on the market. It does not only detect falling edge, it also samples the start bit (uses algorithm mentioned above), if value 0 is sampled, then the start bit is validated. if not, it regards the falling edge as noise then searches another falling edge.
By validation the start bit, it has a much better noise immunity, but for RS485 bus in idle state, this method still has some drawbacks:
- If the noise width is near half of bit, it may be regarded as start of bit.
- If there are 2 noise signals, the second one occurs near 1/2 bit after first one. then both falling edge and start bit validation are satisfied.
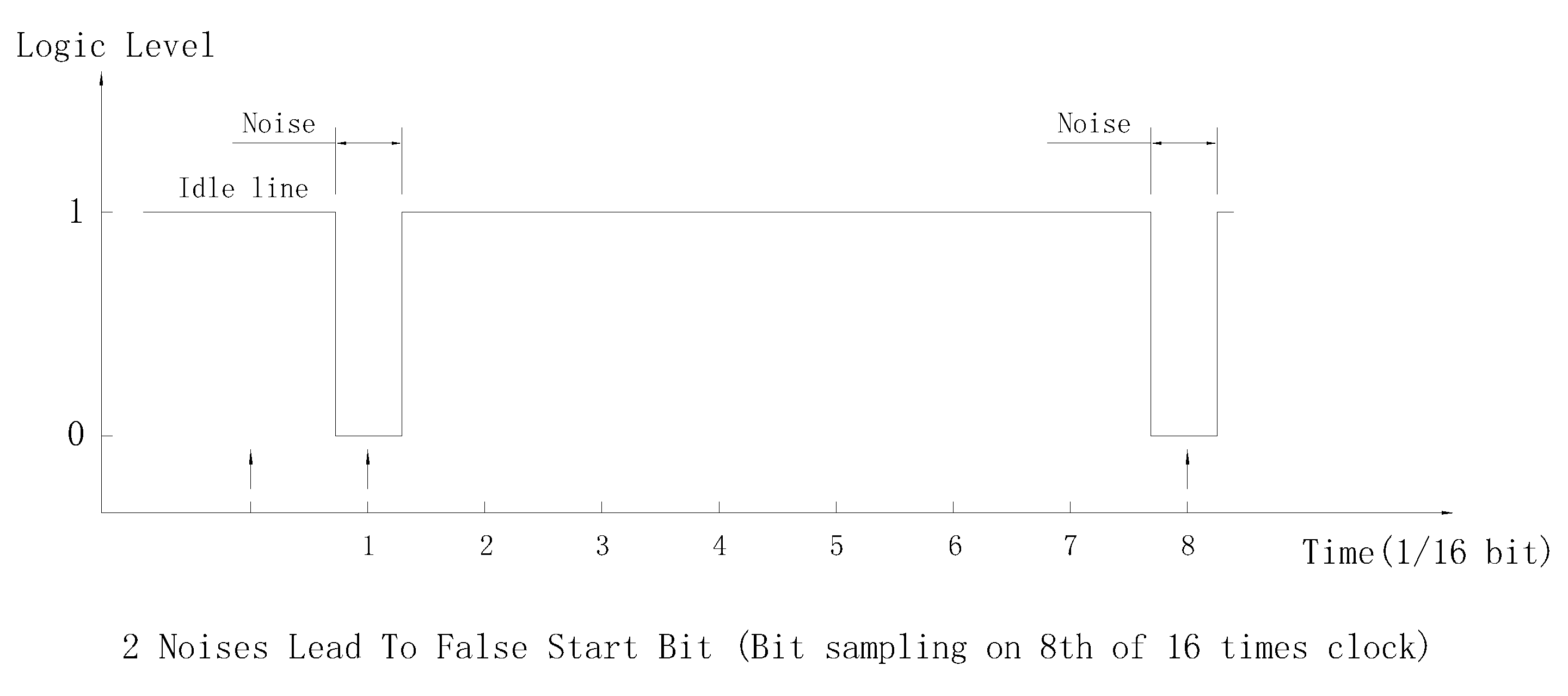
- If the noise signal occurs less than 1/2 bit ahead of falling edge of real start bit. The middle start bit sample will read real start bit and pass validation. So the detected start bit will be ahead of real start bit to 1/2 bit most, that may cause error on later data bit sampling.
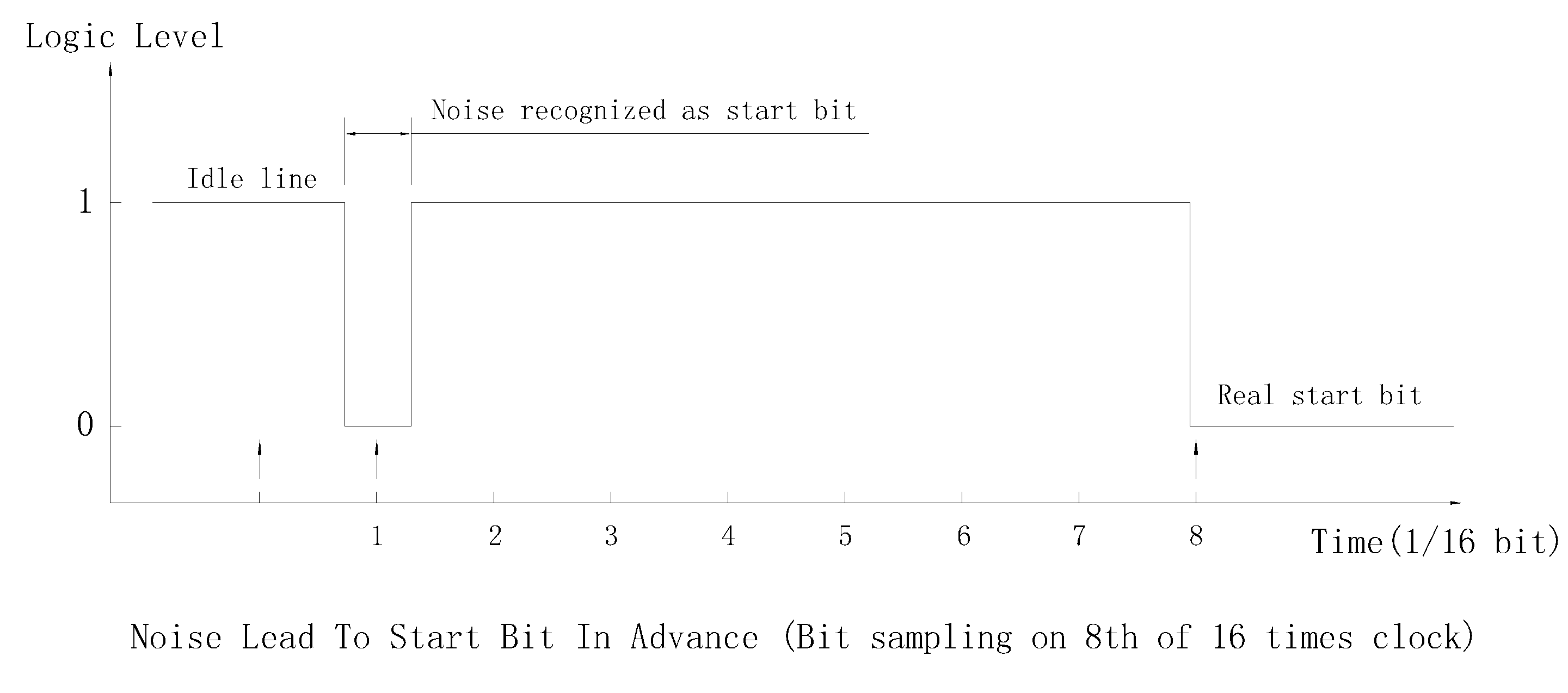
Detect Start Bit With Other Complicated Algorithms
MCUs from STMicroelectronics and Freescale (now NXP) have a complicate Algorithms to detect start bit, all three criteria below should be satisfied:
- A: Falling edge should has 3 leading 1.
- B: At least 2 samples of 0 should be found on 3th, 5th, 7th of clock.
- C: At least 2 samples of 0 should be found on 8th, 9th, 10th of clock.
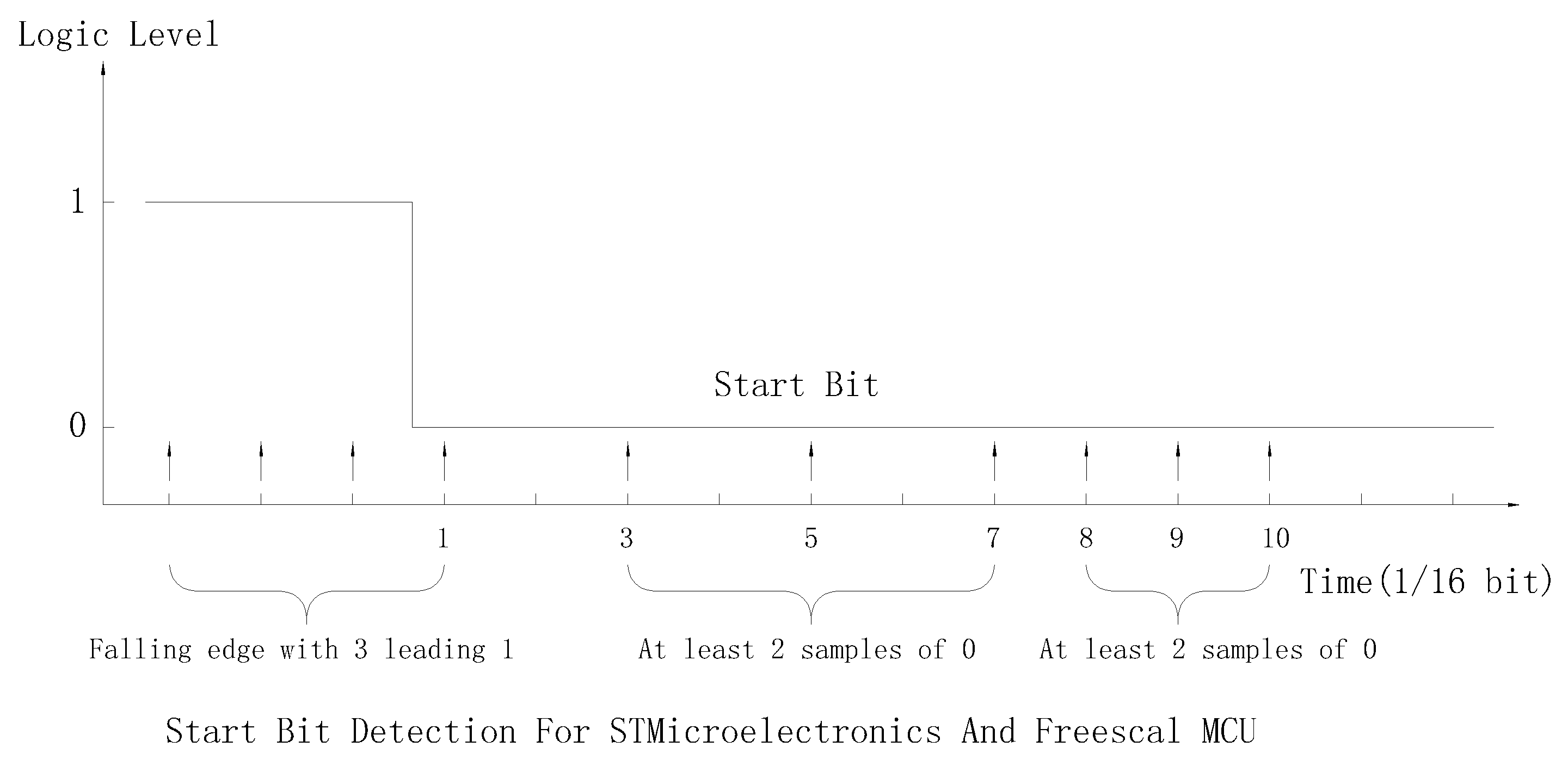
This algorithms works very well in noisy environment, but complicated algorithms usually lead to bug, For example: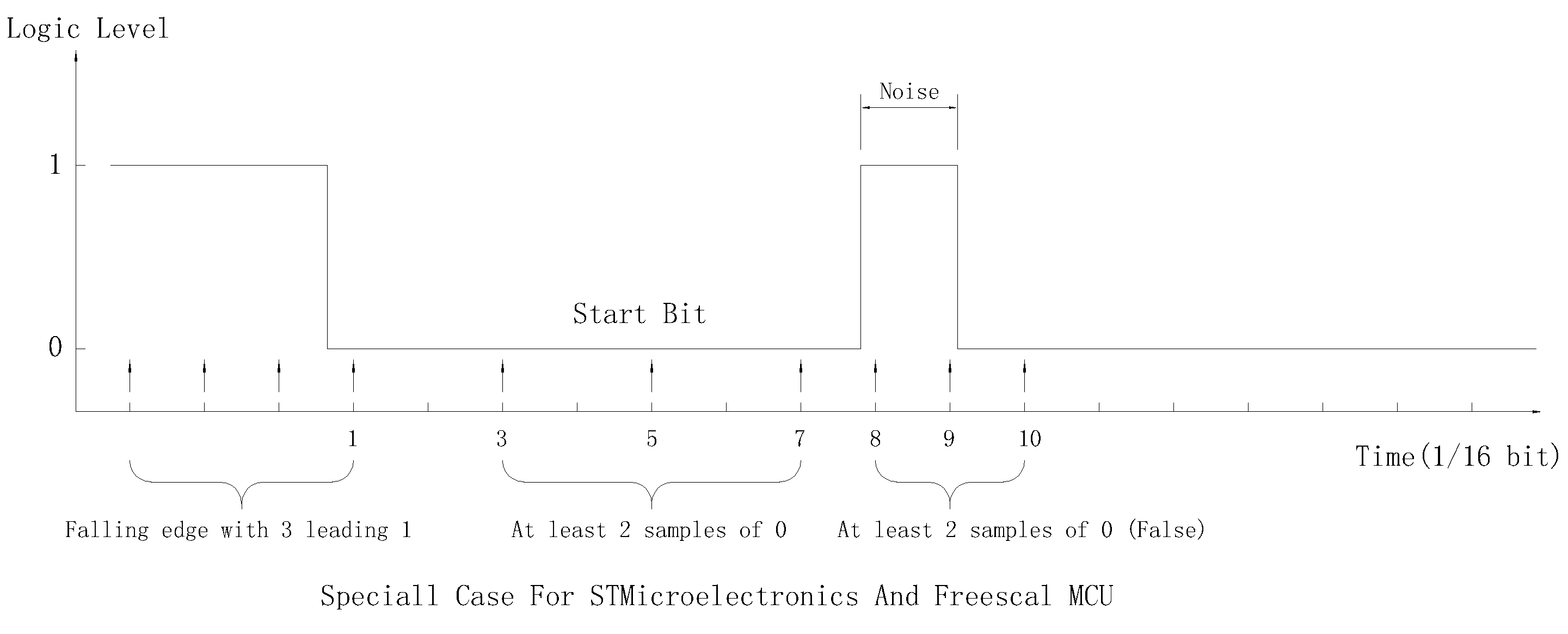
When logic level switches from 1 to 0, a noise wider than 1/16 bits occurs at specific position. The falling edge at 1th clock will not meet rule C, so the decoder will skip it and search other falling edge, because there is no other falling edge meeting rule A, no start bit will be detected. (It had been confirmed on STM32F072RB)
Algorithm Of BACRouter From v6.00+
We implement a 32 times oversampling filter, for each slide window with 32 samples, if the number of 1 is greater than 21, value 1 is outputted, if the number of 1 is less than 11, value 0 is outputted, otherwise the value same as previous slide window is outputted.
Then the bit sampling and detection of start bit will be very simple. Every bit is sampled at the middle of bit. The start bit detection need to search for the falling edge only.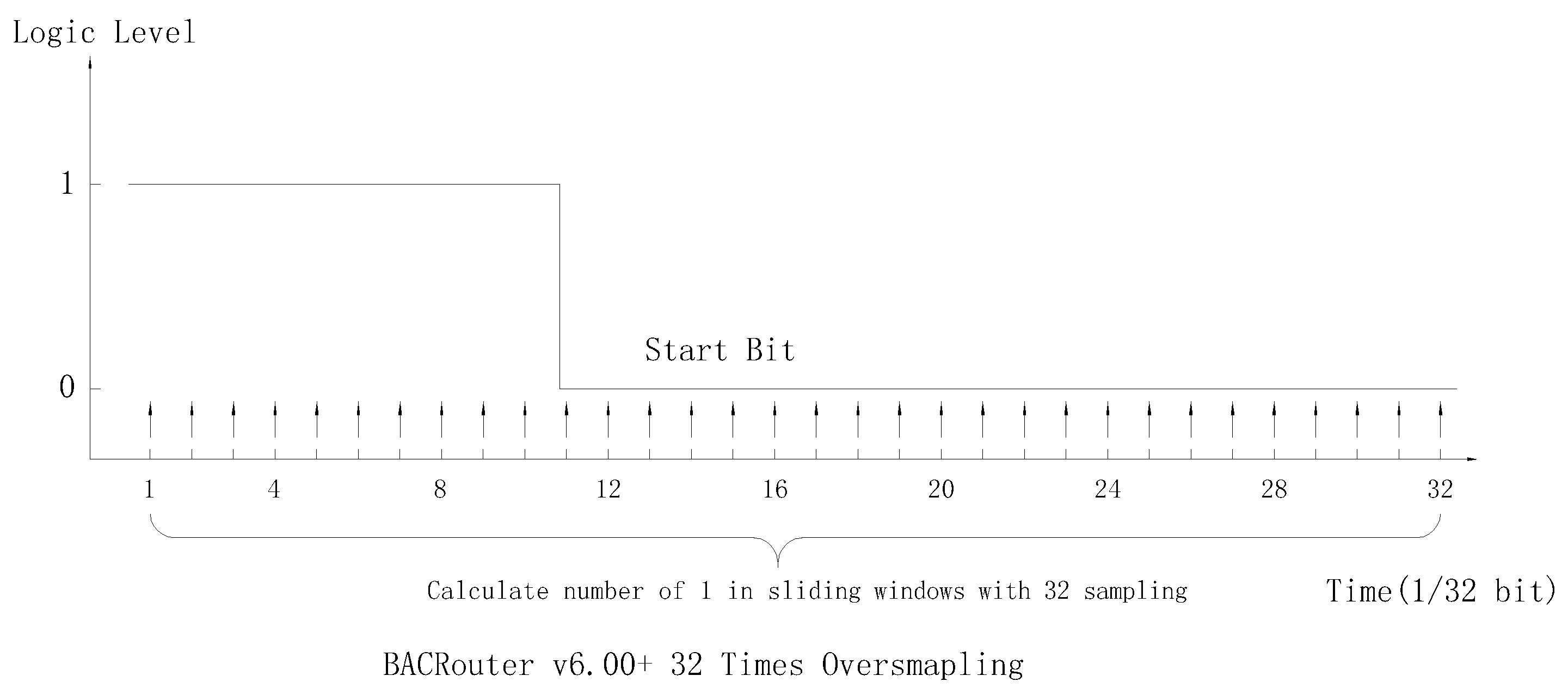 2025.10.15: To achieve better performance when start bit is interfered by noise, or there is baud rate difference between sender and receiver, We implement start bit adjusting by every edge.
2025.10.15: To achieve better performance when start bit is interfered by noise, or there is baud rate difference between sender and receiver, We implement start bit adjusting by every edge.
This algorithm has excellent noise immunity:
- Noise width less than 2/3 bit will not lead to false start bit on a idle RS485 bus.
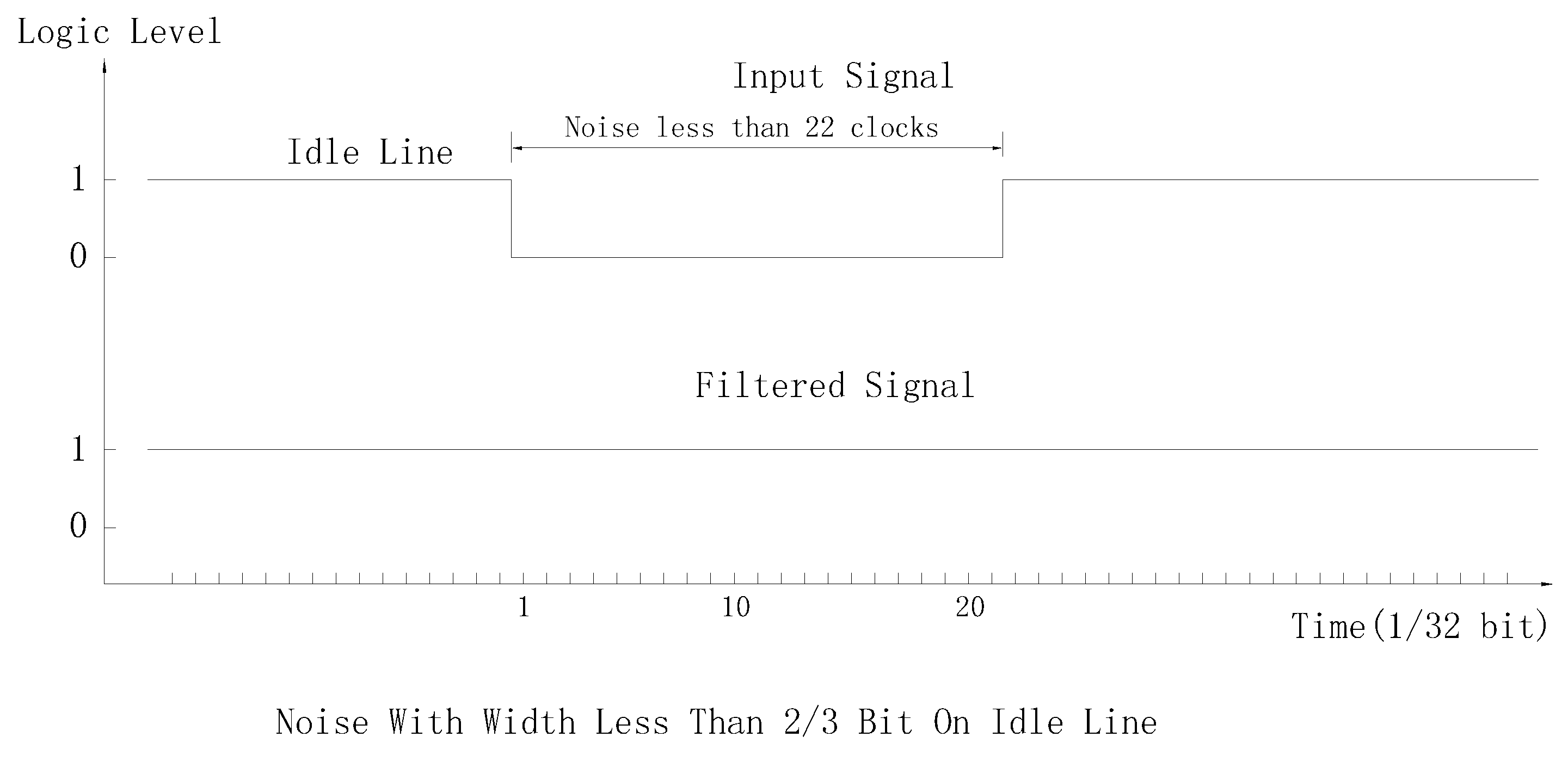
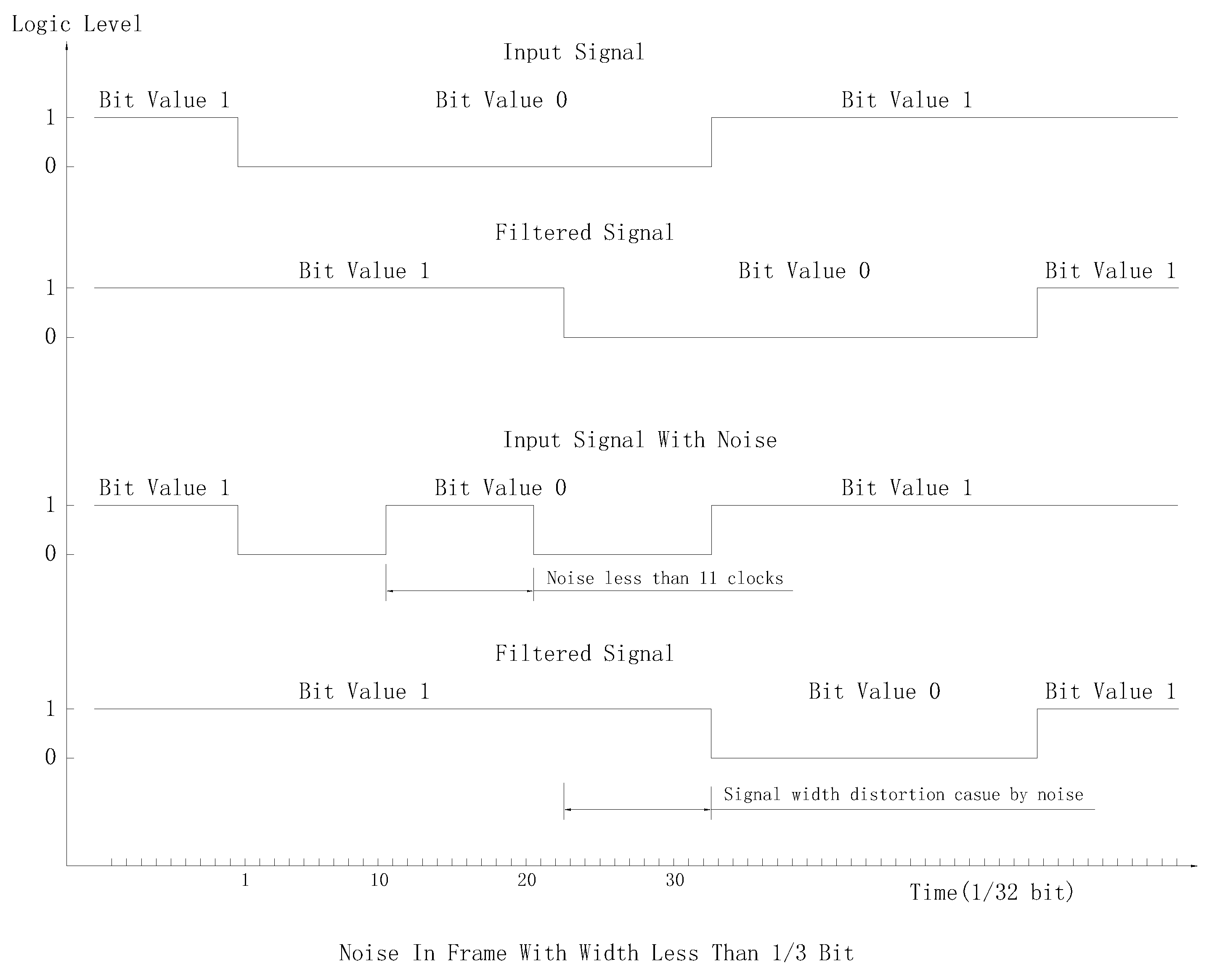
- Noise width less than 1/3 bit will not affect bit sampling
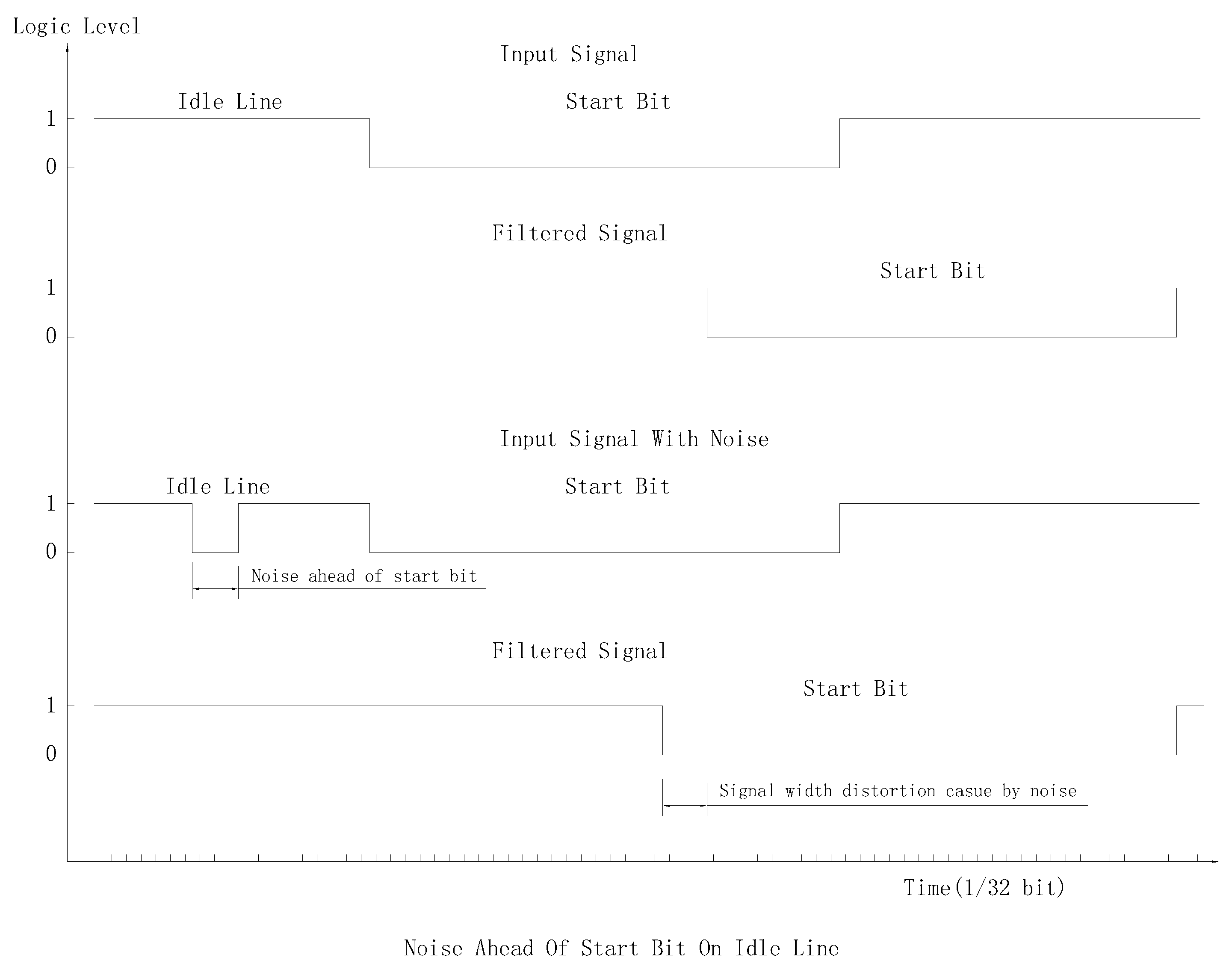
- Noise ahead of real start bit will only advance decoded start bit.
The only situation that it performs worse than traditional decoder is that the noise width or signal distortion is more than 1/3 bit and signal at the middle of bit is still valid.