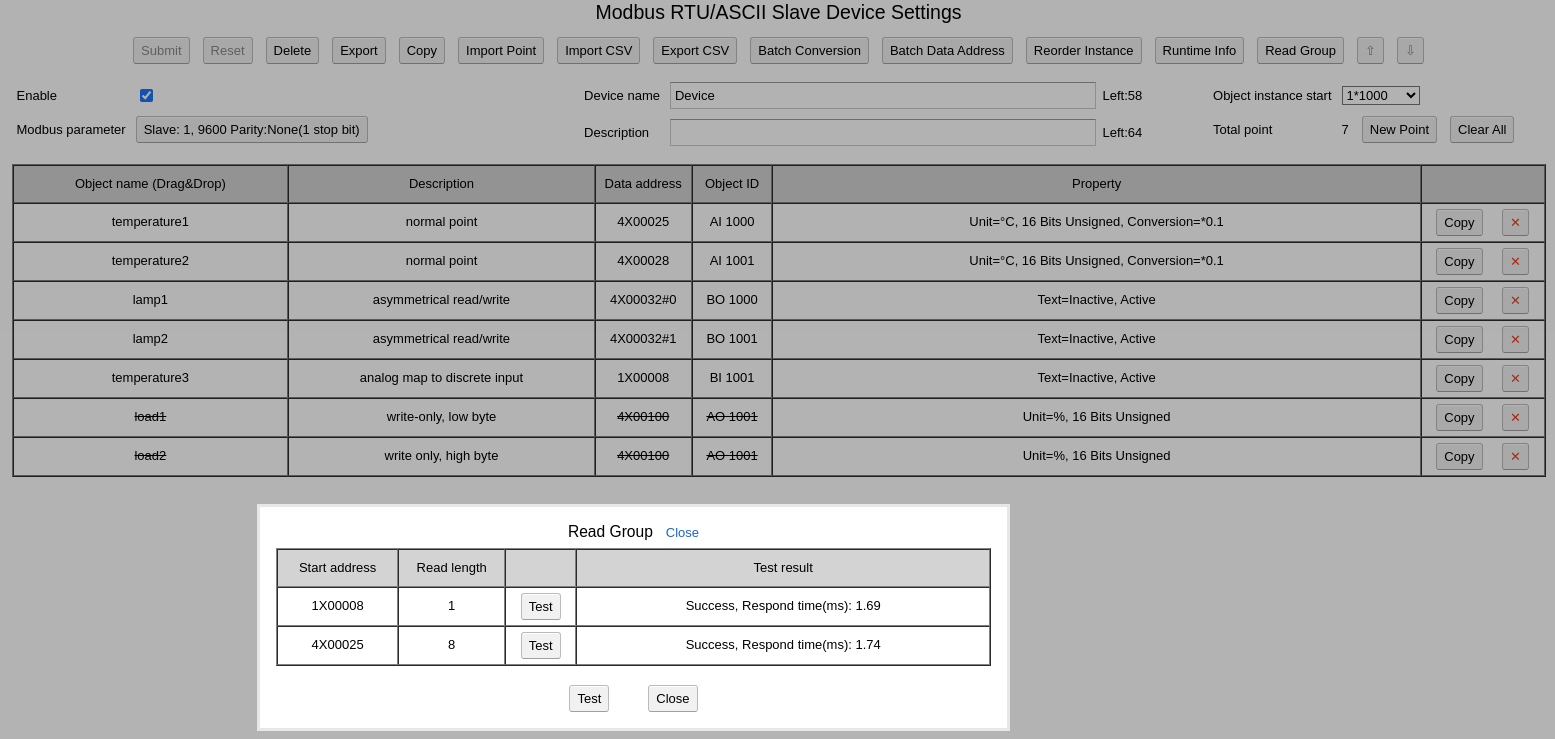
M-Bus or Meter-Bus is a European standard (EN 13757-2 physical and link layer, EN 13757-3 application layer) for the remote reading of water, gas or electricity meters.
The detail of M-Bus could be found here: https://m-bus.com/documentation
The implementation of M-Bus gateway in BACRouter refers to libmbus, Currently we only support serial. TCP is not supoorted yet.
There is very few M-Bus devices in China, so we can not test our implementation well. If you find any bug, please share with us.
To communicate with M-Bus devices, you need a M-Bus/RS485 signal converter.
Scan Records In A Meter:
In libmbus, there are some very useful tools, we have cross-compiled some of them to Win32 platform:
mbus-serial-scan.exe: Scan M-Bus devices on the bus by primary address (0~250)
Usage: mbus-serial-scan.exe -b 2400 COM3
2400 is baudrate. COM3 is the serial port.
mbus-serial-scan-secondary.exe: Scan M-Bus devices on the bus by secondary address
Usage: mbus-serial-scan-secondary.exe -b 2400 COM3
mbus-serial-switch-baudrate.exe: Switch the baudrate of a M-Bus device
Usage: mbus-serial-switch-baudrate.exe -b 2400 COM3 Address Newbaudrate
Address could be a primary address or a secondary address, which could be obtained from previous scan.
mbus-serial-set-address.exe: Set the primary address of a M-Bus device
Usage: mbus-serial-set-address.exe -b 2400 COM3 Address NewPrimaryAddress
mbus-serial-request-data-multi-reply.exe: Pull all records from a M-Bus device
Usage: mbus-serial-request-data-multi-reply.exe -b 2400 COM3 Address
Records pulled will be listed as:
<DataRecord id="1">
<Function>Instantaneous value</Function>
<StorageNumber>0</StorageNumber>
<Unit>Energy (10 Wh)</Unit>
<Value>288144</Value>
<Timestamp>2024-04-07T12:01:21Z</Timestamp>
</DataRecord>
We can just focus on the record id and unit.
Setup Free Client In The BACRouter:
Upgrade the firmware in the BACRouter to version 5.04 or larger.
Connect the RS485 port to the M-Bus, If there is a MS/TP port running on the RS485 port, you should disable the MS/TP port first.
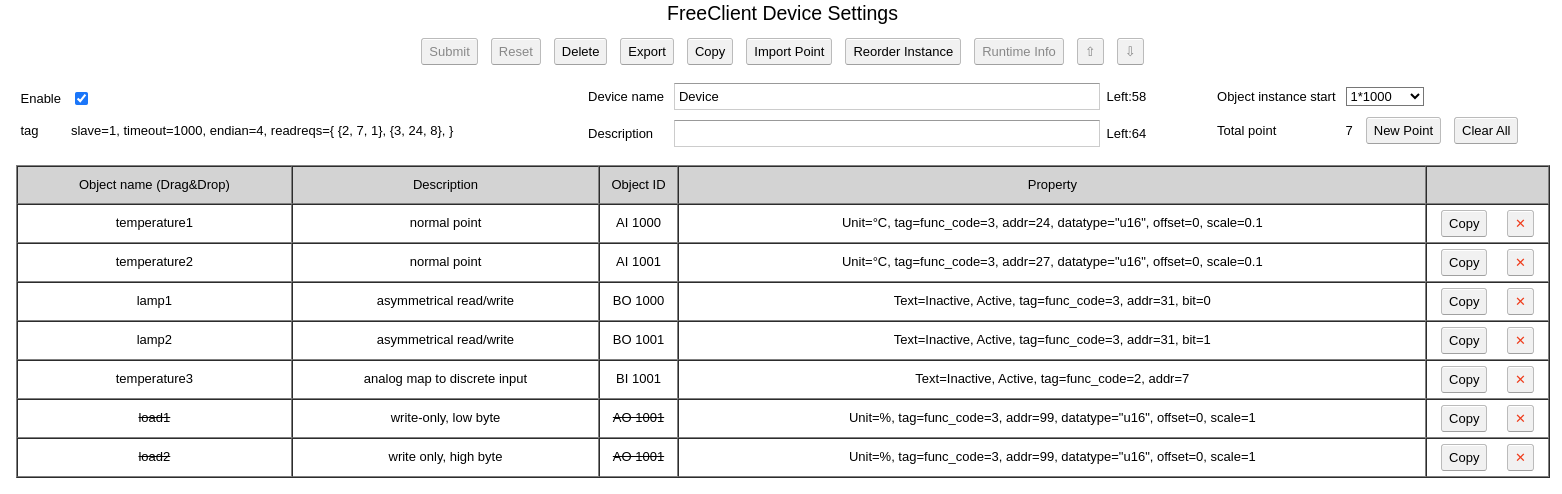
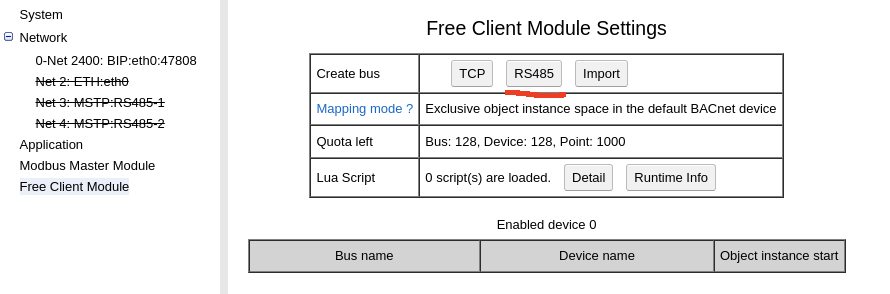
Open WebUI by web browser, select “Free Client Module”, on the “Create bus” row, click “RS485”
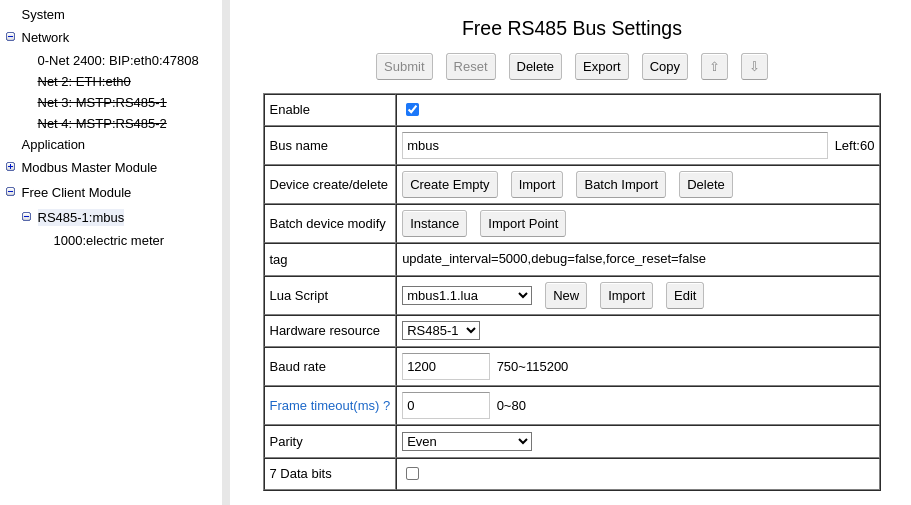
After bus is created, edit the bus:
Note: BACRouter can not support baudrate 300 and 600
From firmware version 5.X, more than one bus can be defined on the same RS485 port. Most RS485 protocol is stateless, so it is safe to do so. But for M-Bus, the sequence of communication is critical, so Don’t define more than one M-Bus on a RS485 port.
The Lua script could be downloaded from here: mbus1.2.lua
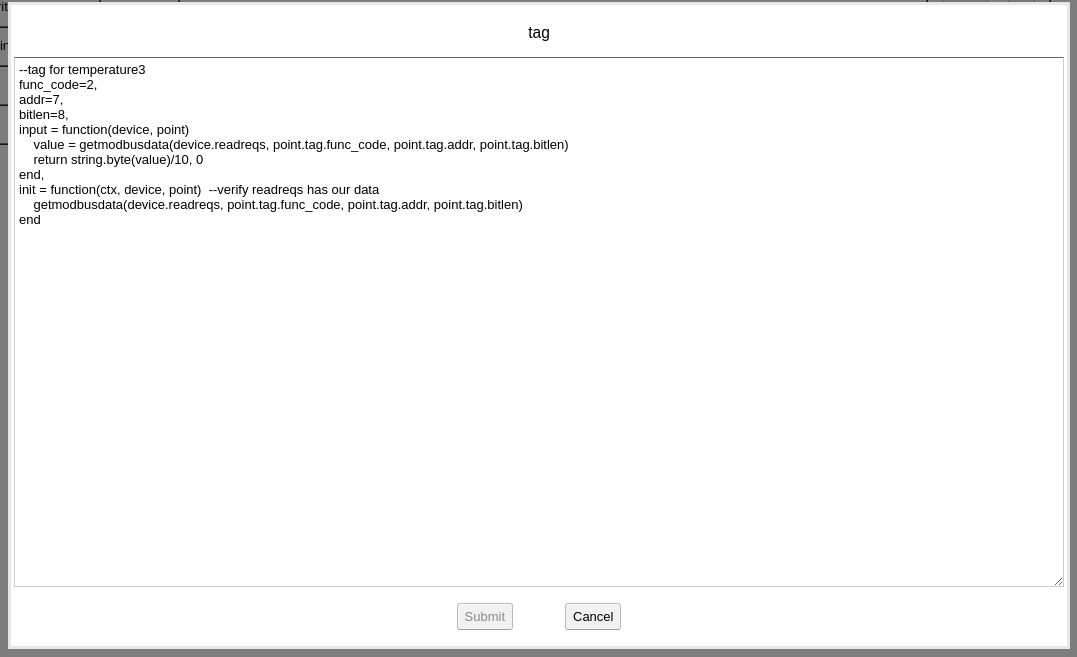
On the “tag” field, update_interval=5000, means every 5000 milliseconds, BACRouter will refresh all values. If force_reset is set, before BACRouter try to communicate with a M-Bus device by primary address, BACRouter will send a “SND_NKE” to the address, which will initialize the device. There was report that some devices only worked under force_reset=true.
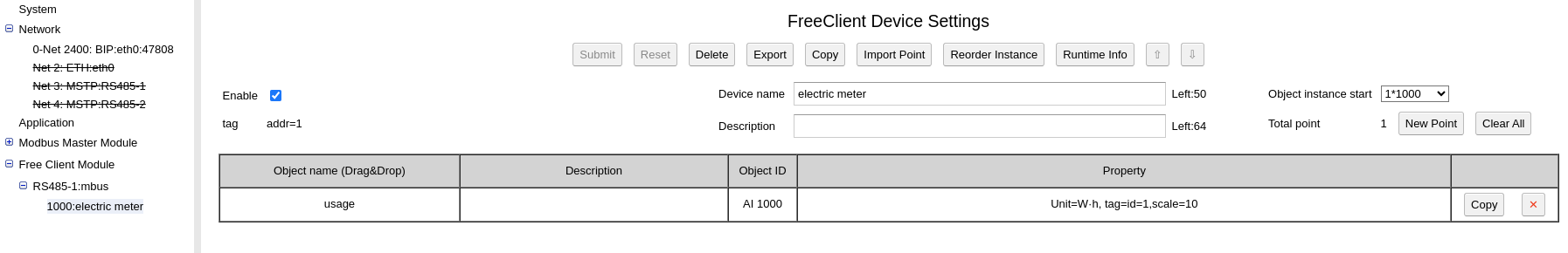
On the “Device create/delete” row, click “Create Empty” to create a new M-Bus device. select created device to edit:
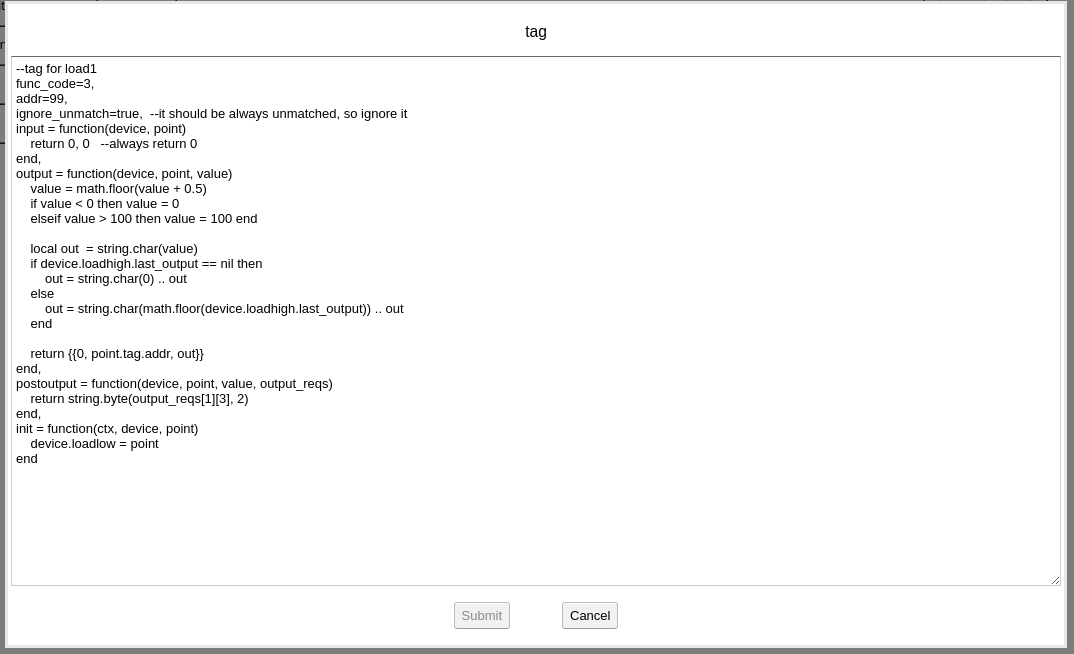
On the “tag” field, input: addr=1
That means the primary address of the M-Bus device is 1, if you want to use secondary address, it should look like: addr=”f57072162440f102″
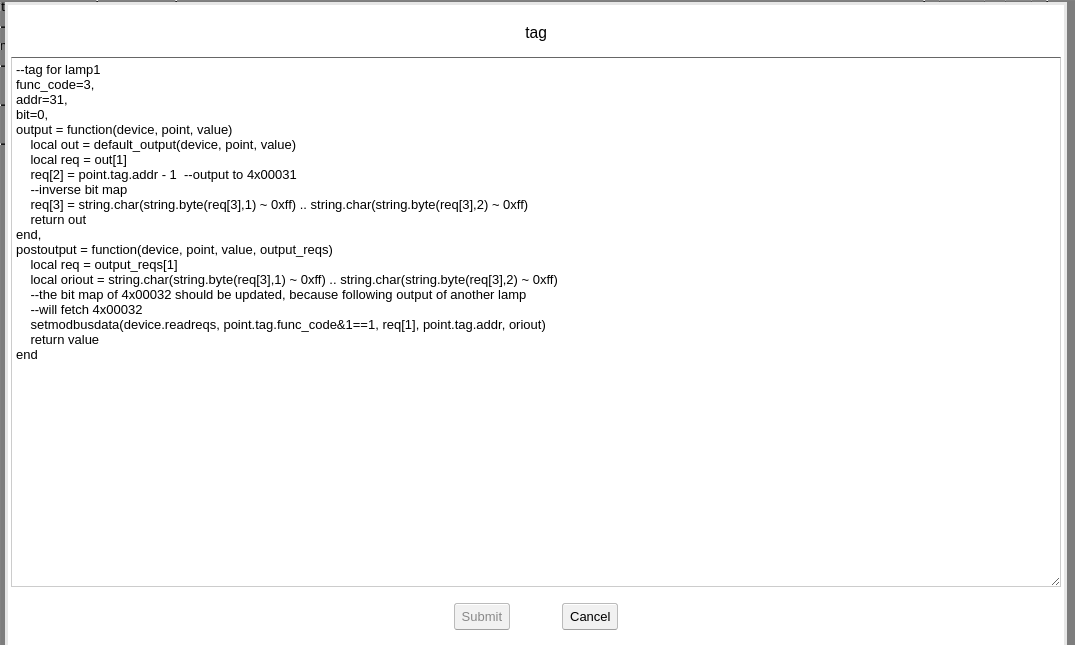
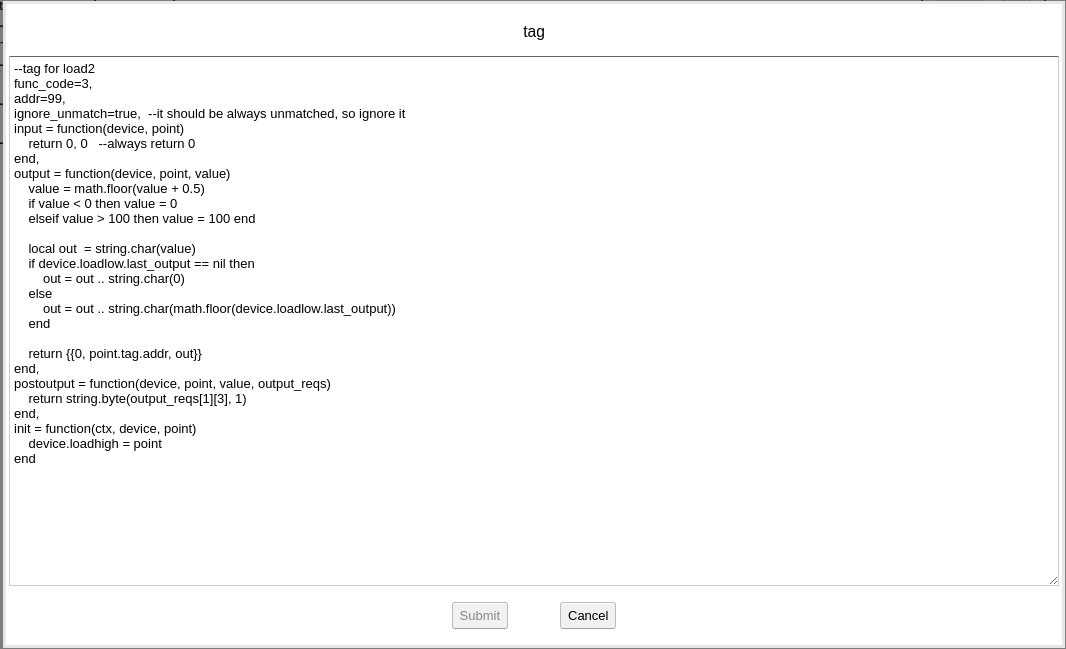
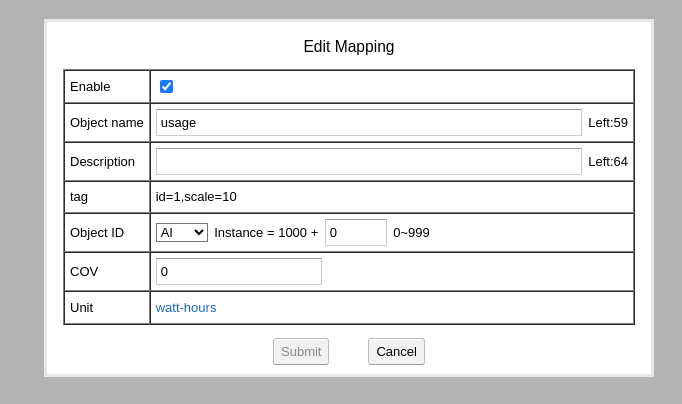
The create a new point to map record id 1, click to edit:
On the “tag” field, id=1 means the record id is 1, scale=10 means the value read from device will be multiplied with 10. Note: the unit of record id 1 is 10 Wh, the BACnet unit we choosed here is Wh.
Example Of M-Bus Configuration
The config of the above M-Bus bus can be downloaded here: RS485-1_mbus.json